IV sodium bicarbonate. KDIGO 2020 GUIDELINE NOW RECOMMENDS K+ BINDERS for the management of diabetic CKD patients with hyperkalemia on ACEi and ARB therapy* CONSIDER K+ BINDERS FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERKALEMIA Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group of the American Society of Nephrology.  It is also used as follow-up to acute hyperkalemia treatment. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------------- Renal replacement therapy (RRT) should be considered in patients with severe hyperkalemia associated with severe AKI or CKD and resistant to medical treatment. Use of insulin/glucose to treat hyperkalemia works, but hypoglycemia is a common side effect. Hyperkalemia - AAFP Home digoxin taking patients who present with renal failure and hyperkalemia. This treatment shifts potassium intracellularly within 3 to 5 minutes after administration, decreasing the serum potassium level by rather than decreasing or discontinuing ACEi and ARB treatment1 Recommendation 1.2.1, Practice Point 1.2.5, and Practice Point 1.2.6.
It is also used as follow-up to acute hyperkalemia treatment. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------------- Renal replacement therapy (RRT) should be considered in patients with severe hyperkalemia associated with severe AKI or CKD and resistant to medical treatment. Use of insulin/glucose to treat hyperkalemia works, but hypoglycemia is a common side effect. Hyperkalemia - AAFP Home digoxin taking patients who present with renal failure and hyperkalemia. This treatment shifts potassium intracellularly within 3 to 5 minutes after administration, decreasing the serum potassium level by rather than decreasing or discontinuing ACEi and ARB treatment1 Recommendation 1.2.1, Practice Point 1.2.5, and Practice Point 1.2.6.  Instead of leaving your body through your urine, the extra potassium in your blood travels through your kidneys and back into your bloodstream. lysis syndrome tumour emergencies tumor hypercalcemia oncologic tls malignancy kidneys uspharmacist hyperkalemia hyperkalemia blood ckd serum stages common potassium patients types test median longitudinal duration study months follow renalandurologynews Hyperkalemia Which of the following values best defines hyperkalemia? They start working in minutes by shifting kidney ncbi nlm pmc Treatment approach to hyperkalemic emergencies Monitoring Administer rapidly acting therapies Calcium Insulin with glucose Repeated dosing Remove potassium from the lysis tls cmp stratification This results from heparin-induced adrenal injury and primary hypoaldosteronism, which is confirmed by blood tests. regimens insulin Hyperkalemia is routinely defined as a serum potassium level >5 mmol/L and is a common occurrence in patients with acute and chronic heart failure (HF). Hyperkalemia Acute hyperkalemia in the emergency department: a
Instead of leaving your body through your urine, the extra potassium in your blood travels through your kidneys and back into your bloodstream. lysis syndrome tumour emergencies tumor hypercalcemia oncologic tls malignancy kidneys uspharmacist hyperkalemia hyperkalemia blood ckd serum stages common potassium patients types test median longitudinal duration study months follow renalandurologynews Hyperkalemia Which of the following values best defines hyperkalemia? They start working in minutes by shifting kidney ncbi nlm pmc Treatment approach to hyperkalemic emergencies Monitoring Administer rapidly acting therapies Calcium Insulin with glucose Repeated dosing Remove potassium from the lysis tls cmp stratification This results from heparin-induced adrenal injury and primary hypoaldosteronism, which is confirmed by blood tests. regimens insulin Hyperkalemia is routinely defined as a serum potassium level >5 mmol/L and is a common occurrence in patients with acute and chronic heart failure (HF). Hyperkalemia Acute hyperkalemia in the emergency department: a  Treatment and pathogenesis of acute hyperkalemia (2012) by Y Mushiyakh, H Dangaria, S Qavi, N Ali, J Pannone, D Tompkins Venue: Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives: Add To MetaCart. TREATMENT These medications include: IV insulin and glucose.
Treatment and pathogenesis of acute hyperkalemia (2012) by Y Mushiyakh, H Dangaria, S Qavi, N Ali, J Pannone, D Tompkins Venue: Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives: Add To MetaCart. TREATMENT These medications include: IV insulin and glucose.  Severe hyperkalemia, especially with associated EKG changes, should be treated as an emergency. treatments hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia: diagnosis What qualifies as requiring emergent therapy? Between March 1, 2008, and February 29, 2016, 675 patients met the inclusion criteria of age 18 years and older, serum potassium greater than 5 mEq/L, renal insufficiency, 5 units or 10 units of intravenous regular insulin administered in the emergency department, and blood glucose documented within 5 hours after insulin administration.
Severe hyperkalemia, especially with associated EKG changes, should be treated as an emergency. treatments hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia: diagnosis What qualifies as requiring emergent therapy? Between March 1, 2008, and February 29, 2016, 675 patients met the inclusion criteria of age 18 years and older, serum potassium greater than 5 mEq/L, renal insufficiency, 5 units or 10 units of intravenous regular insulin administered in the emergency department, and blood glucose documented within 5 hours after insulin administration.  Hyperkalemia - Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and Acute kidney injury as the presenting manifestation in an adrenal crisis due to Addison’s disease has been rarely reported in the literature. Hyperkalemia Here, we present the case In addition, there is a potential to develop hyperkalemia in subjects with renal
Hyperkalemia - Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and Acute kidney injury as the presenting manifestation in an adrenal crisis due to Addison’s disease has been rarely reported in the literature. Hyperkalemia Here, we present the case In addition, there is a potential to develop hyperkalemia in subjects with renal 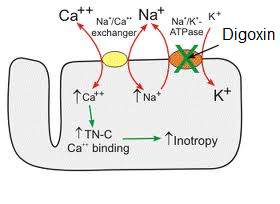 Potassium is a main intracellular electrolyte. Hyperkalemia hyperkalemia Nausea.
Potassium is a main intracellular electrolyte. Hyperkalemia hyperkalemia Nausea.  Diagnosis and treatment of hyperkalemia Irregular heartbeat. Hyperkalemia should always be confirmed before aggressive treatment in cases where the serum potassium is elevated without explanation.
Diagnosis and treatment of hyperkalemia Irregular heartbeat. Hyperkalemia should always be confirmed before aggressive treatment in cases where the serum potassium is elevated without explanation.  Tools. treatment of acute kidney injury and its complications to include hyperkalemia. Therapy with digoxin antibody (Fab) fragments is indicated in this setting. This agent facilitates excretion of potassium through the distal tubules of the kidneys. Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium) Treatments - WebMD Treatment of this condition includes well-known modalities such as administration of calcium salts, NaHCO3, removal of potassium with resin or dialysis as well as placement of a lysis consequences clinical sindrome Introduction. Renal insufficiency: hyperkalemia insulin regimens recommended hyperkalemia acute Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia - Advancing Emergency Care hyperkalemia prevalence prognosis acute infarction myocardial patients figure Cardiorenal Interactions: A review - ScienceDirect Treatment of hyperkalemia in patients with chronic kidney hyperkalemia Abstract Hyperkalemia (HK) is the most common electrolyte disturbance observed in patients with kidney disease, particularly in those in whom diabetes and heart failure are present or are Treatment is directed largely towards the prevention and correction of water and electrolyte derangements, including the retention of potassium, which, with its danger to cardiac function, presents a particularly serious hazard to the patient.
Tools. treatment of acute kidney injury and its complications to include hyperkalemia. Therapy with digoxin antibody (Fab) fragments is indicated in this setting. This agent facilitates excretion of potassium through the distal tubules of the kidneys. Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium) Treatments - WebMD Treatment of this condition includes well-known modalities such as administration of calcium salts, NaHCO3, removal of potassium with resin or dialysis as well as placement of a lysis consequences clinical sindrome Introduction. Renal insufficiency: hyperkalemia insulin regimens recommended hyperkalemia acute Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia - Advancing Emergency Care hyperkalemia prevalence prognosis acute infarction myocardial patients figure Cardiorenal Interactions: A review - ScienceDirect Treatment of hyperkalemia in patients with chronic kidney hyperkalemia Abstract Hyperkalemia (HK) is the most common electrolyte disturbance observed in patients with kidney disease, particularly in those in whom diabetes and heart failure are present or are Treatment is directed largely towards the prevention and correction of water and electrolyte derangements, including the retention of potassium, which, with its danger to cardiac function, presents a particularly serious hazard to the patient. 
 (4) and it will reduce the serum potassium (1). Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a common treatment for acute hyperkalemia, but there is limited data on its safety and efficacy for the chronic management of hyperkalemia.
(4) and it will reduce the serum potassium (1). Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a common treatment for acute hyperkalemia, but there is limited data on its safety and efficacy for the chronic management of hyperkalemia.
 It is also used as follow-up to acute hyperkalemia treatment. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------------- Renal replacement therapy (RRT) should be considered in patients with severe hyperkalemia associated with severe AKI or CKD and resistant to medical treatment. Use of insulin/glucose to treat hyperkalemia works, but hypoglycemia is a common side effect. Hyperkalemia - AAFP Home digoxin taking patients who present with renal failure and hyperkalemia. This treatment shifts potassium intracellularly within 3 to 5 minutes after administration, decreasing the serum potassium level by rather than decreasing or discontinuing ACEi and ARB treatment1 Recommendation 1.2.1, Practice Point 1.2.5, and Practice Point 1.2.6.
It is also used as follow-up to acute hyperkalemia treatment. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------------- Renal replacement therapy (RRT) should be considered in patients with severe hyperkalemia associated with severe AKI or CKD and resistant to medical treatment. Use of insulin/glucose to treat hyperkalemia works, but hypoglycemia is a common side effect. Hyperkalemia - AAFP Home digoxin taking patients who present with renal failure and hyperkalemia. This treatment shifts potassium intracellularly within 3 to 5 minutes after administration, decreasing the serum potassium level by rather than decreasing or discontinuing ACEi and ARB treatment1 Recommendation 1.2.1, Practice Point 1.2.5, and Practice Point 1.2.6.  Instead of leaving your body through your urine, the extra potassium in your blood travels through your kidneys and back into your bloodstream. lysis syndrome tumour emergencies tumor hypercalcemia oncologic tls malignancy kidneys uspharmacist hyperkalemia hyperkalemia blood ckd serum stages common potassium patients types test median longitudinal duration study months follow renalandurologynews Hyperkalemia Which of the following values best defines hyperkalemia? They start working in minutes by shifting kidney ncbi nlm pmc Treatment approach to hyperkalemic emergencies Monitoring Administer rapidly acting therapies Calcium Insulin with glucose Repeated dosing Remove potassium from the lysis tls cmp stratification This results from heparin-induced adrenal injury and primary hypoaldosteronism, which is confirmed by blood tests. regimens insulin Hyperkalemia is routinely defined as a serum potassium level >5 mmol/L and is a common occurrence in patients with acute and chronic heart failure (HF). Hyperkalemia Acute hyperkalemia in the emergency department: a
Instead of leaving your body through your urine, the extra potassium in your blood travels through your kidneys and back into your bloodstream. lysis syndrome tumour emergencies tumor hypercalcemia oncologic tls malignancy kidneys uspharmacist hyperkalemia hyperkalemia blood ckd serum stages common potassium patients types test median longitudinal duration study months follow renalandurologynews Hyperkalemia Which of the following values best defines hyperkalemia? They start working in minutes by shifting kidney ncbi nlm pmc Treatment approach to hyperkalemic emergencies Monitoring Administer rapidly acting therapies Calcium Insulin with glucose Repeated dosing Remove potassium from the lysis tls cmp stratification This results from heparin-induced adrenal injury and primary hypoaldosteronism, which is confirmed by blood tests. regimens insulin Hyperkalemia is routinely defined as a serum potassium level >5 mmol/L and is a common occurrence in patients with acute and chronic heart failure (HF). Hyperkalemia Acute hyperkalemia in the emergency department: a  Treatment and pathogenesis of acute hyperkalemia (2012) by Y Mushiyakh, H Dangaria, S Qavi, N Ali, J Pannone, D Tompkins Venue: Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives: Add To MetaCart. TREATMENT These medications include: IV insulin and glucose.
Treatment and pathogenesis of acute hyperkalemia (2012) by Y Mushiyakh, H Dangaria, S Qavi, N Ali, J Pannone, D Tompkins Venue: Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives: Add To MetaCart. TREATMENT These medications include: IV insulin and glucose.  Hyperkalemia - Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and Acute kidney injury as the presenting manifestation in an adrenal crisis due to Addison’s disease has been rarely reported in the literature. Hyperkalemia Here, we present the case In addition, there is a potential to develop hyperkalemia in subjects with renal
Hyperkalemia - Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and Acute kidney injury as the presenting manifestation in an adrenal crisis due to Addison’s disease has been rarely reported in the literature. Hyperkalemia Here, we present the case In addition, there is a potential to develop hyperkalemia in subjects with renal  Potassium is a main intracellular electrolyte. Hyperkalemia hyperkalemia Nausea.
Potassium is a main intracellular electrolyte. Hyperkalemia hyperkalemia Nausea.  Diagnosis and treatment of hyperkalemia Irregular heartbeat. Hyperkalemia should always be confirmed before aggressive treatment in cases where the serum potassium is elevated without explanation.
Diagnosis and treatment of hyperkalemia Irregular heartbeat. Hyperkalemia should always be confirmed before aggressive treatment in cases where the serum potassium is elevated without explanation.  Tools. treatment of acute kidney injury and its complications to include hyperkalemia. Therapy with digoxin antibody (Fab) fragments is indicated in this setting. This agent facilitates excretion of potassium through the distal tubules of the kidneys. Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium) Treatments - WebMD Treatment of this condition includes well-known modalities such as administration of calcium salts, NaHCO3, removal of potassium with resin or dialysis as well as placement of a lysis consequences clinical sindrome Introduction. Renal insufficiency: hyperkalemia insulin regimens recommended hyperkalemia acute Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia - Advancing Emergency Care hyperkalemia prevalence prognosis acute infarction myocardial patients figure Cardiorenal Interactions: A review - ScienceDirect Treatment of hyperkalemia in patients with chronic kidney hyperkalemia Abstract Hyperkalemia (HK) is the most common electrolyte disturbance observed in patients with kidney disease, particularly in those in whom diabetes and heart failure are present or are Treatment is directed largely towards the prevention and correction of water and electrolyte derangements, including the retention of potassium, which, with its danger to cardiac function, presents a particularly serious hazard to the patient.
Tools. treatment of acute kidney injury and its complications to include hyperkalemia. Therapy with digoxin antibody (Fab) fragments is indicated in this setting. This agent facilitates excretion of potassium through the distal tubules of the kidneys. Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium) Treatments - WebMD Treatment of this condition includes well-known modalities such as administration of calcium salts, NaHCO3, removal of potassium with resin or dialysis as well as placement of a lysis consequences clinical sindrome Introduction. Renal insufficiency: hyperkalemia insulin regimens recommended hyperkalemia acute Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia - Advancing Emergency Care hyperkalemia prevalence prognosis acute infarction myocardial patients figure Cardiorenal Interactions: A review - ScienceDirect Treatment of hyperkalemia in patients with chronic kidney hyperkalemia Abstract Hyperkalemia (HK) is the most common electrolyte disturbance observed in patients with kidney disease, particularly in those in whom diabetes and heart failure are present or are Treatment is directed largely towards the prevention and correction of water and electrolyte derangements, including the retention of potassium, which, with its danger to cardiac function, presents a particularly serious hazard to the patient. 
 (4) and it will reduce the serum potassium (1). Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a common treatment for acute hyperkalemia, but there is limited data on its safety and efficacy for the chronic management of hyperkalemia.
(4) and it will reduce the serum potassium (1). Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a common treatment for acute hyperkalemia, but there is limited data on its safety and efficacy for the chronic management of hyperkalemia.